
Early developments in silane coupling agents began in the mid-20th century, closely tracing the rise of composite materials in manufacturing. Chemists searching for robust links between organic polymers and inorganic fillers eventually landed on the utility of methacrylate-functional silanes. By the 1970s, as the global demand for stronger, lighter, and more durable materials grew, this specialized organosilane found its way into high-performance applications, from aerospace to dental resins. Researchers in my academic circle often referenced patents from Dow Corning and Shin-Etsu that brought structure, tighter purity standards, and greater transparency to the production process. Companies frequently cited collaborative efforts with academic institutions to dial in the best formulations for practical use. Veterans from the plastic and adhesive industries will remember debates from the 1980s, at trade shows and in professional journals, on tweaking silane functionalities to target new resin systems or improve weatherability in coatings.
3-(Methacryloxy)Propylmethyldiethoxysilane, known to many lab technicians as an essential coupling agent, bridges the gap between mineral surfaces and resins. Formulators of glass-filled plastics swear by it for improving strength and moisture tolerance. Laboratories value the dual nature of its methacrylate and silane groups, which enable integration into both organic matrices and inorganic surfaces. Personal experience as a chemist taught me that even small additions can transform the handling and processing of composite blends. This compound rarely gains the type of public recognition given to more glamorous additives, but ask any shop foreman who views improved bonding or filler dispersion as a big win.
The compound has an oily, nearly colorless appearance, making visual checks straightforward. It emits a faint, characteristic odor, neither overpowering nor pungent, but enough to remind you of the need for vigilant ventilation. With a molecular weight hovering around 278 g/mol, it boasts a boiling point close to 260°C. The molecule itself doesn’t dissolve in water, but it hydrolyzes slowly, thanks to those diethoxy groups, which break down and release ethanol upon exposure to moisture. Handling it in production requires respect for its reactivity; without temperature control, it can polymerize—something newcomers discover quite quickly if left unchecked. Its density, slightly higher than water, and characteristic refractive index both contribute to straightforward quality checks during incoming inspections.
Commercial suppliers label drums with chemical name, CAS number 13501-76-3, UN shipping codes, batch numbers, and relevant hazard pictograms. Typical minimum purity sits above 97% when coming from reputable producers, with residual solvents and byproducts like alcohols drawing sharp attention from QC auditors. The label includes shelf life, recommended storage in cool, dry conditions, and warnings about moisture sensitivity. Safety Data Sheets from the likes of Sigma-Aldrich state concentration ranges for safe use, reinforce the need for gloves and goggles, and describe spill cleanup with focus on ethanol vapor formation. Every decent warehouse manager I’ve known keeps a logbook for siloed storage away from acids, bases, and oxidizers.
On the factory floor, production hinges on the hydrosilylation of methacryloxypropene, where methyl-diethoxysilane serves as the silane donor. Skilled operators measure catalyst and reactants with care to maximize conversion and minimize side products. Reaction vessels run under moderate temperatures and controlled pressure, with inert gas blankets used throughout to avoid premature polymerization. Recovered product undergoes vacuum distillation, refined to strip out unreacted materials and stabilize the functional silane. In my own plant walk-throughs, juggling yield against energy use always factored heavily into process improvements—nobody likes a batch with off-spec color or pungency.
The true appeal of this compound lies in its dual-reactivity. The methacrylate group undergoes radical polymerization, slotting seamlessly into acrylic polymer chains. The silane end hydrolyzes, bonds with hydroxyl groups on glass, silica, alumina, or filler particles. Customizing polymer properties often means modifying or blending it with other silanes. Adjustment of pH during application lets users tune hydrolysis rates, something I found invaluable for keeping working times predictable during trial formulations in the lab. Some researchers add inhibitors to the reaction mixture to slow unwanted pre-reactions, preserving shelf life without compromising on end-use performance.
Industry catalogs list it under several synonyms. Common variants include Methacryloyloxypropylmethyldiethoxysilane, A-175, Silarine 1747, and Silquest Y-11878. Some suppliers simply describe it by its function: methacrylate silane coupling agent. Distributors in Asia-Pacific give it local brand names, though regulatory filings rely on IUPAC. For procurement teams, matching the right synonym with regional supply documents often proves a tedious but necessary part of global sourcing.
The material warrants respect both in the lab and on the shop floor. Inhalation of vapors leads to headaches or respiratory irritation, with chronic exposure raising risk of dermatitis. Spill cleanup grows complicated quickly if ethanol levels spike or surfaces aren’t sealed. OSHA sets tight guidelines for handling volatile organosilanes, and any seasoned EHS officer will point to the importance of flame-proof storage, spill kits, and negative air pressure in handling zones. Manual transfer under poor ventilation carries real risk—witness the array of near misses logged in plant safety audits during annual reviews. Environmental managers often push for secondary containment and prompt registration of any releases, not just for air quality but groundwater concerns as well.
This compound turns up in products that touch everyday life and advanced industries alike. Plastics manufacturers rely on it to improve the strength and water resistance of fibreglass-reinforced parts. Adhesive formulators add it to dual-cure systems so that glass-fabric composites actually stay together under stress. Construction sealants see boosted adhesion to concrete or metal surfaces. Dental labs and prosthetics specialists swear by it for making resins that bond firmly without swelling or yellowing after curing. Researchers in surface modification tests often use it to improve printability or anti-fouling properties of films. I’ve encountered projects in the renewable energy sector, where coats with this silane improve adherence of solar cell layers, letting panels endure tough weather and handling.
New research concentrates on sustainable sourcing, with green chemistry groups looking to cut down the generation of hazardous byproducts in manufacturing. Academics study substitution patterns on the silane backbone to bring custom properties to specialty polymers. Research grants from both governments and private foundations recently targeted improved hydrolytic stability, opening up marine and underwater applications. I’ve sat through countless conference seminars on plasma treatment and UV-modified silanes, as researchers race to create coatings with specific optical or antimicrobial features. Universities push collaborative development with manufacturers, focusing on rapid property screening and long-term durability tests beyond traditional ASTM protocols.
Toxicology teams keep a close eye on occupational exposure risks. Inhalation studies in rats and rabbits show low acute toxicity, yet skin contact does produce mild to moderate irritation according to EU REACH dossiers. Chronic exposure, especially among production line staff, carries risk of sensitization, so routine skin checks and PPE still matter. Environmental testing finds rapid breakdown of the compound in soil and water, easing long-term persistence concerns, though tests in aquatic species show heightened vigilance for runoff near sensitive watersheds. In several cases, risk assessors flagged the side-production of ethanol, which leads to cumulative atmospheric VOCs—a longstanding concern for anyone living downwind of manufacturing sites. Continued data sharing between regulatory agencies and producers plays a big part in aligning health standards across continents.
The next decade will see more demand for this silane in advanced composite manufacturing, lightweight automotive panels, and wind energy components. Research teams in Japan and the US test new blend partners to boost UV stability and reduce production costs. As circular economy initiatives take root, producers turn to bio-based raw materials and closed-loop manufacturing. Custom silanes with added reactivity or longer open-times could give adhesives and sealants further reach into niche sectors like electronics assembly or energy storage. In my own consulting experience, customers rarely stand still—requests for improved impact resistance, thermal stability, or green labeling keep suppliers innovating. Regulators balance the need for tighter chemical stewardship with industry’s push for faster adoption, making nimble R&D and transparent safety data sharing more valuable than ever.
Years ago, a friend handed me a part from his new carbon fiber bike. He raved about its strength and lightness, but never mentioned what made those materials lock together so well. Only later, after working in a lab developing composite resins, did I learn that a compound called 3-(Methacryloxy)Propylmethyldiethoxysilane often plays a huge role in connecting resin and glass or carbon surfaces. This compound belongs to the family of silane coupling agents that give modern composites their bite.
The main job of 3-(Methacryloxy)Propylmethyldiethoxysilane? It acts like a translator between two groups that typically struggle to communicate—organic polymers and inorganic materials, especially glass fibers. On one side of its molecule sits a methacrylate group, ready to bond with acrylic or epoxy systems found in paints, adhesives, and plastics. On the other, a pair of ethoxy groups reacts with the hydroxyl groups lining glass surfaces.
In practical terms, this means the silane gives fiberglass-reinforced plastics a much stronger grip. I’ve cracked open failed parts before: with the silane, the break runs through the glass instead of slipping at the surface. Without it, the resin lets go first, and the part crumbles. Silanes like this one have triggered leaps in performance for wind turbine blades, circuit boards, and lightweight auto parts.
You’ll spot 3-(Methacryloxy)Propylmethyldiethoxysilane behind the scenes in construction sealants, concrete treatments, and waterproof coatings too. In each case, it helps organic resins hold tight to mineral-based surfaces. Take concrete repair: enhancing the bond between patching compounds and old concrete keeps cracks closed far longer. Formulators in paint companies use this molecule to improve scrub-resistance and extend the life of exterior coatings under punishing sun and rain.
Anyone working in electronics may have seen its role in printed circuit boards. There, it helps resins adhere to glass cloth, which allows for thinner, smaller, and tougher products. Its chemical backbone fits right into today’s push for miniaturization—nobody wants to carry around a brick-sized phone anymore.
Concerns about chemical exposure aren’t rare in manufacturing. Silanes are no exception. I introduced extra ventilation at the bench after learning these molecules can irritate skin and eyes. Good handling practices, gloves, and ventilation make a difference. It also helps that, in the end-use product, silanes create a stable bond and don’t leach or outgas under normal conditions. Proper training and respect for safety data sheets go a long way.
Seeking stronger composites without hazardous ingredients? Chemists constantly work on greener alternatives and safer processing routes. Waterborne systems cut down on solvents, while new silane variations deliver performance with less risk and environmental impact. People invent better surface prep techniques too—laser or plasma treatments that further boost adhesion without depending solely on chemistry.
In my time in materials labs, few things rival the impact of a tiny molecule that bridges worlds. 3-(Methacryloxy)Propylmethyldiethoxysilane might sound technical or obscure, but it quietly strengthens everything from wind turbines to dental fillings. It’s worth noticing the silent power that makes tomorrow’s breakthroughs possible.
Anyone who’s ever watched a product recall unfold understands just how serious storage and handling really are. One missed step can turn a valuable product into a liability. My background includes managing a small pharmacy storeroom, so I’ve seen up close how temperature, moisture, and light affect what’s on the shelves. If the back room runs a few degrees warmer, half the insulin stock loses effectiveness. Stories like that turn guidelines about cool, dry places and sealed containers into mission-critical action steps.
The FDA and similar agencies update storage requirements constantly, because even slight deviations can put people in harm’s way. In the industry, we track critical details. These don’t just come from lab experiments but from situations where products hit real-world conditions—floods, power outages, air conditioning failures. One time, a shipment of vaccines got delayed at an airport without climate control. Every box spoiled, leading to both waste and public risk. Think about it: money down the drain, clinics scrambling, and families left unprotected.
A simple number on a box can spell out a world of trouble. An upper limit like 25°C looks easy enough until summer rolls in or a shipment crosses three states in one day. According to a report from the World Health Organization, about 20% of global temperature-sensitive products get mishandled somewhere between production and the end-user—usually because the supply chain underestimated storage stakes. Spending a little more on controlled storage beats the fallout from recalls.
Humidity sneaks up on plenty of products. One leaky pipe, even for an hour, can turn cardboard packaging soft and let pests and mold in. I’ve opened containers only to find ruined stock because someone overlooked a slow, steady drip over the weekend. A simple fix—installing clear labels and monitoring devices—goes a long way.
No fancy system works without people who understand what’s at stake. A good warehouse team remembers that a forgetful employee can cost the company thousands or even millions. Training forms the backbone. I’ve led sessions where a new team member arrived straight from another industry, not knowing why gloves and masks matter around pharmaceuticals. A two-hour workshop changed her approach, and she caught an error the very next week.
Mistakes slip through cracks when employees believe short cuts won’t hurt. The truth is, every step in handling—lifting, stacking, labeling—adds up. Whether a product stays safe relies on everyone from the driver to the stock clerk thinking about every detail, every shift.
Technology helps, but blind trust in barcodes or sensors won’t fix problems built into warehouse culture. Real improvement always comes from connecting simple actions with long-term impact. The companies who do this best hold regular check-ins and use real incident stories instead of dry rules. They invest in temperature monitoring systems that send alerts to supervisors’ phones. In my experience, giving the team the right tools and enough information motivates them to catch small issues before they get big.
Product safety depends just as much on detailed handling instructions as on the materials themselves. Everyone from manufacturers to end-users needs clear, practical training on real-world risks and solutions. Keeping shelves organized, storage rooms monitored, and staff engaged turns these rules into a line of defense that protects both the bottom line and the community.
Working with polymers often gives you a front-row seat to the challenges of making chemicals play nicely together. In labs and on factory floors, people seek ways to bridge chemistry’s natural divides. 3-(Methacryloxy)propylmethyldiethoxysilane, usually called by the easier nickname “methacryloxy silane,” shows up right in the thick of this challenge. Unlike many obscure compounds, this silane doesn't sit on the shelf looking impressive and doing nothing. Professionals in adhesives, paints, and specialty plastics often reach for it to make tough blends work.
This compound brings two worlds together: silicon-based and organic-based materials. It sports both a methacryloxy group and ethoxysilane ends. You could think of it as a kind of translator between different chemical languages. Anyone who has tried to bond glass fibers into polyester or vinyl ester resins will know the value of a good silane coupling agent. Methacryloxy silane wins trust in fiberglass-reinforced plastics. Engineers and chemists look for strong adhesion with fewer problems from moisture and temperature changes. Reports from composites manufacturers show sharper performance and longer-lasting bonds where this compound gets used.
You don’t need to be a PhD chemist to run into compatibility headaches. A typical day on a manufacturing line could see someone mixing resin, waiting for it to set, and then noticing poor adhesion or surface defects. Here’s where methacryloxy silane steps up. It connects with many resins—epoxies, polyesters, and acrylics especially—because its structure includes reactive sites that are eager to join up during curing. Industry case studies help back this up. For example, a switch from untreated fillers to silane-treated ones in SMC/BMC molding compounds often brings better mechanical strength.
Every user learns quickly that not all blends take kindly to every additive. Some polymers, such as pure polyolefins, lack the functional groups needed for strong bonding with silanes. Polypropylene or polyethylene without prior modification often shrugs off methacryloxy silane’s advances. Sometimes, extra steps like plasma treatment or chemical grafting must clear the way. Nothing replaces in-house trials. Even with positive lab data, the quirks of a production process may shift the outcome, depending on humidity, cure temperature, and surface cleanliness.
The key lies in choosing the right partners and fine-tuning conditions. It pays to talk directly with suppliers who have run field trials. They often keep technical bulletins with recommended use levels, blend ratios, and detailed curing schedules. Holistic prep, including primer treatments and carefully controlled environmental conditions, makes a big difference. Independent testing—pull strength, peel adhesion, resistance to aging—lets teams spot problems early. My own experience taught me to test adhesion under both expected and harsh scenarios. Lab and real-world performance often part ways.
Newer polymer blends may call for fresh thinking about compatibilizers and surface treatments. Research labs continue pushing beyond classic glass and resin matchups, seeking ways to make methacryloxy silane work with novel substrates. For end users, clear technical guidance and realistic expectations sit at the core of getting good results. By adjusting process steps and keeping open lines with chemical suppliers, most teams see real gains without major cost increases. Performance, safety, and reliability all improve when people pay close attention to the details.
Working around chemicals brings enough risks that it pays to check the label and read the Safety Data Sheet before even opening the cap. I remember watching a coworker accidentally get splashed with a solvent. The room filled with fumes, and nobody knew which code on the storage shelf matched the chemical. That scene stuck with me. A label isn’t just decoration; even small print about toxicity, flammability, or required gear can save you a trip to the ER.
Some substances give off vapors that irritate the lungs, eyes, and skin long before they show visible signs of damage. Data from the CDC points out that about 13 million workers in the U.S. are exposed to potentially harmful chemicals each year, with many workplace injuries coming from misreading or ignoring precautions.
Rubber gloves, safety goggles, and lab coats may feel awkward at first, but skipping them usually means risking an accident. Anyone working with acids, cleaning agents, or strong solvents knows that long sleeves and eye gear catch the splash that otherwise lands on skin. I once saw someone forget to slip on safety goggles, thinking the task was quick. Five minutes later, a popping container sent liquid straight toward his face. He spent hours getting his eyes flushed. The hospital staff repeated the lesson: safety gear always beats improvising.
If you suspect the chemical could be inhaled or generate dust, a mask with the correct filters matters. Not every mask blocks every vapor—checking if a respirator matches the hazard is part of taking chemicals seriously. According to NIOSH, hundreds of respiratory-related incidents occur because masks don’t fit or filter what they claim.
Spills almost always happen when people rush or underestimate volumes. A spill kit under the counter, clearly marked with absorbent pads, is not a luxury, but a must. Having an eyewash station and a shower within reach can mean the difference between a minor incident and long-term injury. I never store acids with bases or flammable chemicals next to oxidizers—separate shelves block unintended reactions and keep airspace clear.
Chemicals need proper containers with secure lids. A leaky bottle often starts as an unnoticed drip from a loose cap, turning into dangerous fumes or stains that spread underfoot. Labels should always be updated; hand-written or missing dates risk confusion, especially after a few months. OSHA reports show that poor labeling and mixed storage account for a significant portion of chemical accidents on worksites and in classrooms alike.
No policy replaces knowing your limits and asking questions. Seasoned mentors teach new staff the ropes not just as a formality, but so everyone builds habits before a mistake hurts someone. Even after years on the job, I still run through the steps: check for air flow, confirm emergency contacts, and clear clutter before handling anything unfamiliar.
Emergency plans—up-to-date phone numbers, clear routes, and a shared understanding of who handles what—make a world of difference in a crisis. Practicing these steps isn’t about bureaucracy but about keeping real people safe every day. Sticking to these habits and taking time to teach the next person ensures safety isn’t just policy, but standard practice everyone takes seriously.
Dosing looks simple on paper—just check a label or a chart and mix away. Out in the real world, the right amount gets shaped by people’s needs, regulations, and safety margins set after years of research. It’s not just about avoiding too much or too little. It’s about producing a real effect safely, day after day.
I remember years back, as a pharmacy tech, measuring out antibiotics for kids. The pharmacy always stressed: never eyeball it, never round up. Every drop mattered because doses below the recommendation lost their punch against infection, but above it brought stomach cramps, rashes, or worse. I learned that guidelines stick because they protect real lives, not just numbers on studies.
Take over-the-counter pain killers. Ibuprofen for adults often sticks to a 200-400 mg dose every 4-6 hours, never over 1,200 mg in 24 hours without a doctor’s nod. There’s a reason for that: these thresholds come from clinical trials and real hospital admissions—kidney trouble and stomach bleeds climb when folks treat the bottle like popcorn.
Manufacturers of vitamins and food additives can’t print random numbers. For vitamin D, the usual dose hovers around 600-800 IU daily for most adults. Going higher, say over 4,000 IU for long stretches, raises calcium, causes kidney stones, and even weakens bones. My uncle ignored his doctor's suggestion and pushed his supplements over the limit. Months later, blood tests caught it—even good things stack up against you.
Household bleach often comes diluted at 5-6%. This works for disinfecting, but some still chase stronger mixes. Working at a grocery store during a particularly nasty flu season, I saw customers make unwise choices, ignoring label guidance for mixing with water. The fumes filled the air, coughing followed, and one person landed in urgent care. These concentrations came from lessons written in accident reports and safety bulletins.
Hospitals rely on standard doses because deviations either dull the medicine or turn it dangerous. Antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, insulin—they all dance on a razor’s edge. Dosing gets calculated by body weight, age, and sometimes even genetics. One dose fits many, but not all, which is why medical staff double-checks and adjusts, sometimes hour by hour.
People benefit from clear communication. Labels and instructions need straight language and common examples, not just percentages or cryptic abbreviations. Public health campaigns spot gaps—take recent pushes for safer opioid prescribing. These started in the aftermath of years of overuse and misuse, with clear guidance on microgram and milligram dosing for doctors, pharmacists, and patients. Progress shows up slowly in fewer ER visits, less confusion, and healthier communities.
I’ve watched family members, patients, and coworkers take cues from packaging and from their own questions. The best results show up where people know why the numbers matter, how to use a pill, cleaner, or supplement, and when to ask for advice. Recommendations save more than time—they back up health, safety, and trust, dose by dose.
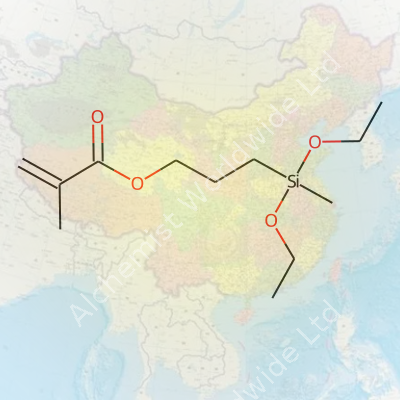

| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | 3-(dimethoxy(ethyl)silyl)propyl 2-methylprop-2-enoate |
| Other names |
KH-572 A-174 Methacryloxypropylmethyldiethoxysilane 3-(Methacryloyloxy)propylmethyldiethoxysilane 3-(Methacryloyloxy)propylmethyldiethoxysilane |
| Pronunciation | /ˌmeθ.əˌkræɪˈlɒk.siˌprəʊ.pɪlˌmeθ.əlˌdaɪˌiːˈθɒk.siˈsaɪ.leɪn/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | [] |
| Beilstein Reference | 1462905 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:88278 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL3722067 |
| ChemSpider | 21285714 |
| DrugBank | DB14497 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 03c6c43c-cf6a-49c0-b330-476bc049c4e5 |
| EC Number | 245-366-4 |
| Gmelin Reference | Gm. 113176 |
| KEGG | C19621 |
| MeSH | D016686 |
| PubChem CID | 69441 |
| RTECS number | GF8750000 |
| UNII | 1I6LN7M387 |
| UN number | UN1993 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID0021694 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C11H22O4Si |
| Molar mass | 248.38 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless transparent liquid |
| Odor | Characteristic |
| Density | 0.97 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| Solubility in water | Insoluble in water |
| log P | 2.2 |
| Vapor pressure | 0.2 mmHg (25 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | pKa ≈ 25 (methacrylate α-proton, estimated) |
| Basicity (pKb) | 3.2 |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.420 |
| Viscosity | 2.5mPa.s (25°C) |
| Dipole moment | 3.07 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 558.6 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | '' |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling | GHS07, GHS08 |
| Pictograms | GHS07, GHS08 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H226, H315, H319 |
| Precautionary statements | P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P271, P273, P280, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P337+P313, P370+P378, P403+P235, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 1-1-0-HEALTH |
| Flash point | > 93 °C |
| Autoignition temperature | 260 °C |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 Oral Rat 11070 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (oral, rat): 8,010 mg/kg |
| NIOSH | GVG63910E7 |
| PEL (Permissible) | PEL (Permissible Exposure Limit) for 3-(Methacryloxy)Propylmethyldiethoxysilane: Not established |
| REL (Recommended) | 1 ppm |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
3-(Trimethoxysilyl)propyl methacrylate 3-(Methacryloxy)propyltrimethoxysilane 3-(Methacryloxy)propyltriethoxysilane γ-Methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane Methacryloxypropylsilanetriol 3-(Methacryloxy)propylmethyldimethoxysilane |